
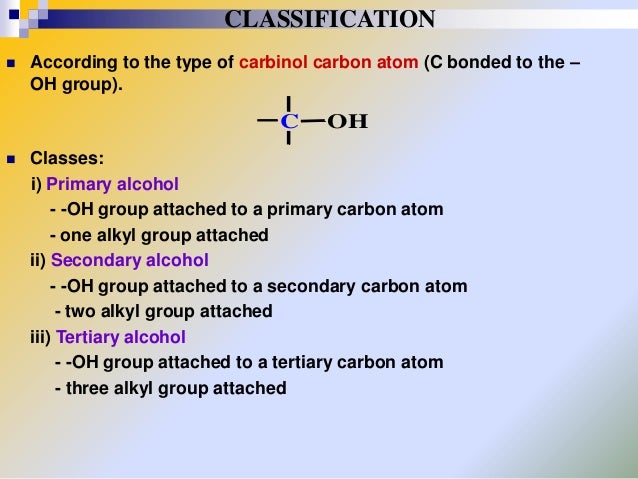
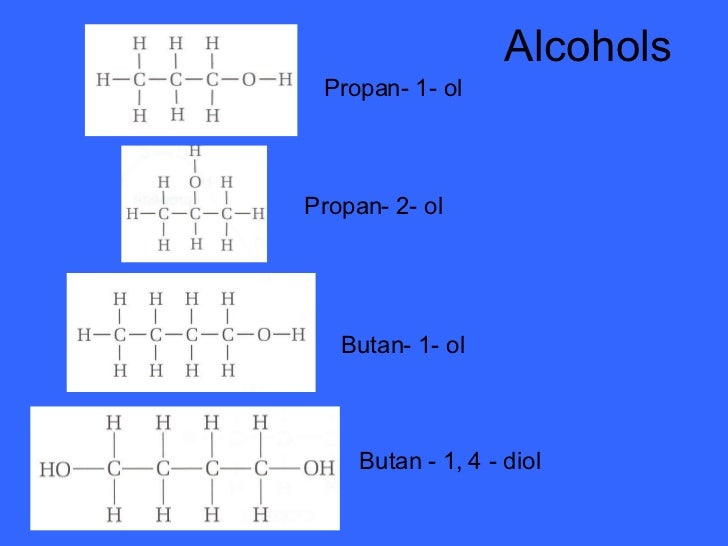
PRIMARY, SECONDARY AND TERTIARY ALCOHOLS
HYDRATION OF ETHENE
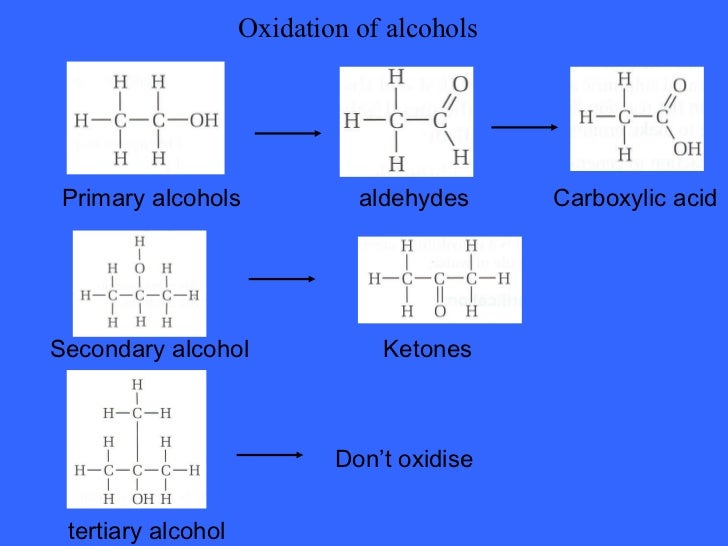
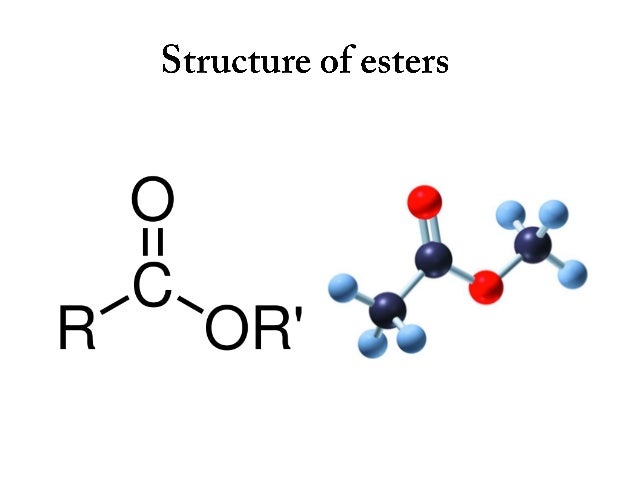


Reactivity of Alcohols towards dehydration : 3 > 2 > 1
When you dehydrate an alcohol, you remove the -OH group, and a hydrogen atom from the next carbon atom in the chain. With molecules like butan-2-ol, there are two possibilities when that happens.
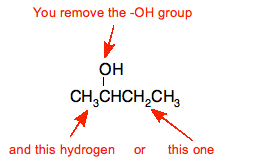
That leads to these products:
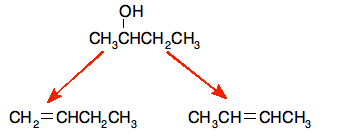
The products are but-1-ene, CH2=CHCH2CH3, and but-2-ene, CH3CH=CHCH3.

Nucleophilic Substitution(Halogenation)
Reaction Of Alcohols:
REFLUX


































No comments:
Post a Comment